(How to correctly understand the meaning of the speed reduction in Apple's "speed-down door"? How much has it dropped?) We discussed the cause of the incident in Apple's speed-down door: the iPhone suddenly shut down at low temperatures. In fact, lithium (ion) batteries not only cause trouble to apples at low temperatures, but Samsung's mobile phones have also been criticized for not being able to charge at low temperatures. My wife's old iPad, after charging this full charge in the winter, will suddenly lose power, and the charger can't be turned on. It will only resume after a while on the heater. It is praised by my daughter as the most expensive. Electronic equipment.
This article focuses on the impact of temperature, especially low temperature on lithium batteries, and some clarification of the misunderstanding of lithium battery use. This article is not the basic principle and development history of the popular battery. Please contact Google if you are interested. There are many interesting stories here. Let us first look at a set of concepts.
Energy Density
The unit of lithium battery capacity is generally "mAh" (mAh) or "Ah" (Ah), and there is a difference between rated capacity and actual capacity when used. Energy density refers to the unit volume or unit weight of the battery, the amount of electricity that can be stored and released. There are two types of units: Wh/kg, Wh/L, which represent the weight ratio energy and volume ratio energy, respectively. At the time of application, the indicator of energy density is more indicative than capacity. The capacity is not enough, it can be bigger, and the increase in energy density requires technological advancement.
The development of lithium batteries has entered a period of slow growth in recent years after experiencing a rapid period. For example, Samsung's average annual energy density increase of 6.5% is far behind Moore's Law in the semiconductor industry:
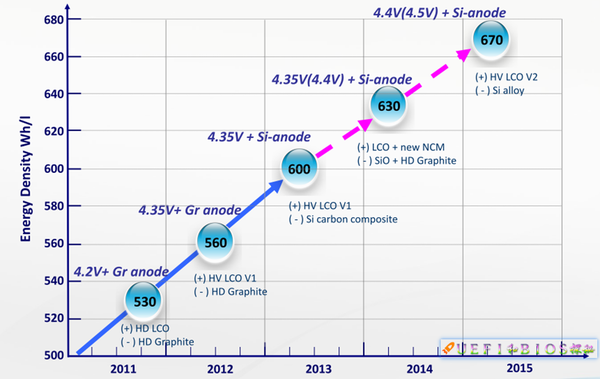
手机的锂电池能量密度已经相当的高:
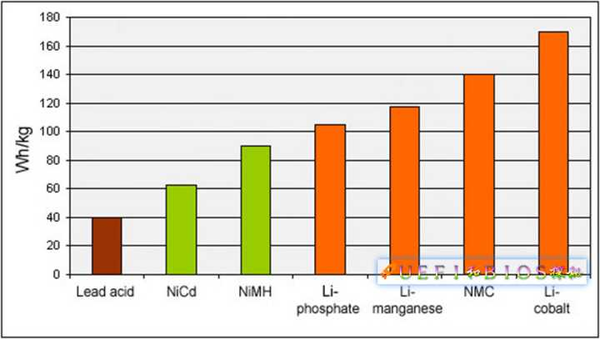
Lithium battery use conditions
Such a high energy density lithium battery, its use must be very careful. A little careless, light impact on life, but may explode, such as Samsung's battery door. Among all the conditions of use, voltage and temperature are the two most important related conditions, as shown below:
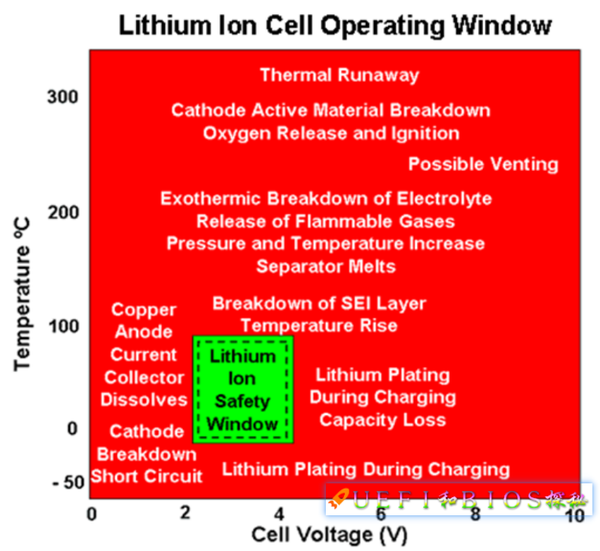
The horizontal axis is the voltage and the vertical axis is the temperature. It can be seen that in this quadrant, the large red color warnings indicating various dire consequences are only a small safe area in the middle. It is the comfort zone of a lithium battery, and it is a risk to leave it:
High voltage and low voltage:
The voltage of a lithium ion battery has an open circuit voltage and an operating voltage, which will not be described in detail herein. The open circuit voltage is usually defined as 3.7V, but after the new battery is fully charged, it can reach 4.2V; after the lithium battery reaches 3.4V, it can be said that there is no power. In fact, 3.0V is really called completely dead. Lithium battery discharge curve:
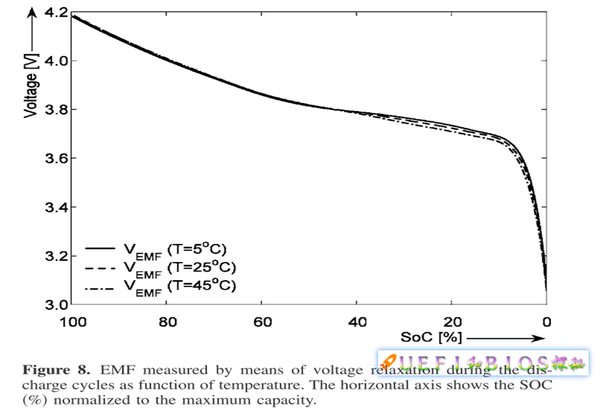
Above 4.2V and below 3.4V will have an impact on lithium battery life. Above 4.2V is called overcharge, which will have an irreversible effect on battery life, which will cause thermal runaway, which may cause bubble, liquid leakage, fire and explosion.
The life of a lithium-ion battery is divided into two parameters: cycle life and calendar life. The calendar life calculation is complicated and the application scene is closely related. Therefore, the Cycle Life is generally used to indicate the number of times the battery can be charged and discharged in cycles. The current battery cycle life is now hundreds of times. The national standard is 300 times.
Below 2.0V is over-discharged, which can seriously affect battery life.
High and low temperature:
Both high temperature and low temperature will affect battery life, as shown in the figure:
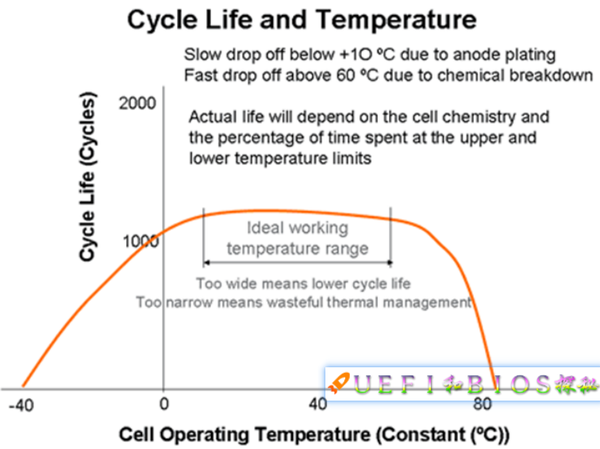
The low temperature causes the internal resistance of the battery cell Cell condensate to decrease, and lithium condensation may form at the cathode, irreversibly affecting the battery life. High temperatures can cause thermal runaways such as explosions. Very dangerous.
Low temperature impact
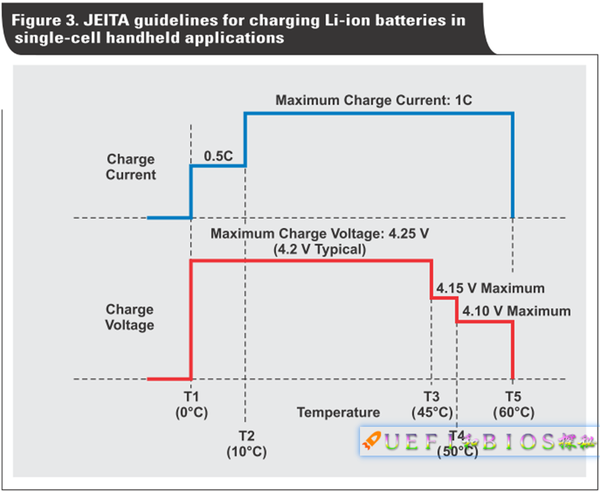
Low temperatures can make charging difficult and dangerous, so charging needs to follow JEITA:
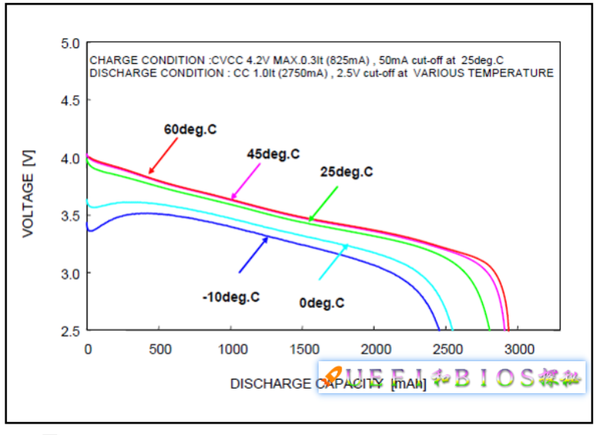
At the same time, the discharge is very rapid at low temperature:
Lithium battery protection
All lithium batteries have self-protection circuitry. A simple protection circuit needs to include at least the following elements:
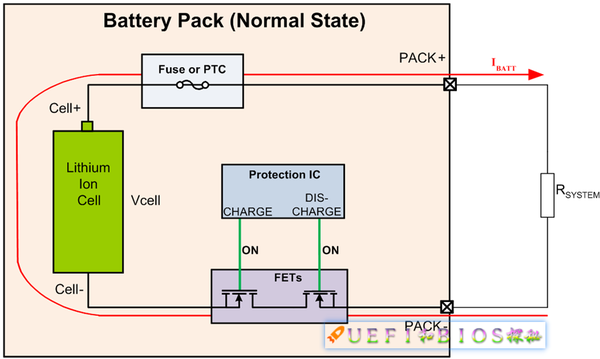
Protection IC: With bidirectional charge and discharge protection, disconnect the circuit during overcharge or overdischarge for safety.
Fuse: The current is blown in an emergency, which is the last insurance.
in conclusion
The use of lithium batteries at low temperatures, regardless of charging or discharging performance is not good, and may have an impact on the life, it should be avoided. Here are some of the public statements in the use of lithium batteries, let's identify them one by one:
The first time you use the full charge three times to activate the lithium battery. Wrong, the lithium battery has no memory effect and does not need to be activated.
It is best to use the light to recharge. Wrong, the cycle life is not a vulgar charge, but an overall Cycle, the process of using the battery and then refilling it, instead of plugging in the charger and unplugging it once. Can be used with the charge. If you use light to rush, placing it for too long may cause over-discharge and affect battery life.
Don't charge all the time, pull it out when you are ready. The small part is correct and most of the errors. A typical mobile phone is not simply a constant voltage charge when charging, but to extend battery life, there are optimized charging algorithms, including CC, CV and MC. After judging the flush, it will not always rush, no need to worry, you can always plug in the power supply. Some cottages and low-cost equipment are recommended to be recharged due to the lack of charging management equipment.
Idle phones should be charged in time. correct. When the lithium battery is not in use, the power will creep away. If it is lower than 2.0V, it will be over-discharged, which seriously affects the battery life. It is best to charge regularly.
other
Finally, the last issue (how to correctly understand the meaning of the speed reduction in Apple's "speed reduction door"? How much has it dropped?) The last question:
Why does Apple explode the frequency reduction problem, but other mobile phone manufacturers do not? Isn't the battery aging?
Here are some of my thoughts (it's hard to say the answer, the answer is in everyone's mind). The first is the fact:
As the number of cycles increases, the lithium battery can provide a peak open circuit voltage that drops slowly, which means that the voltage drops after the charge. The peak current that can be supplied will also drop.
The peak current drops to a certain level and does not provide the power required to peak the power consumption of the handset.
Low temperatures can cause serious problems. This includes a drop in the starting voltage, a steep discharge curve, and so on.
So this is a common problem in the industry. So why is Apple only forced to downgrade? I think that Apple's mobile phone is relatively stable, it is difficult to crash and other problems; at the same time, the user base is large, all generations of mobile phones are in use, my wife and an iPhone4 can also be used to play games; Apple has to support long tail users. And ordinary Android phones, after aging, various problems frequently, for example, Samsung originally had a flash memory door (in fact, many Android phones have similar problems, I will not name it), often crash after a year, no one knows To die (as far as I know, a mobile phone also has a battery aging problem, but choose to ignore).